What is CGI?
CGI, or Computer-Generated Imagery, refers to the creation of digital visuals, characters, environments, or effects using computer software. It’s widely used in films, TV, video games, and advertising to produce realistic or fantastical elements that are impossible, impractical, or too costly to capture with traditional filming techniques.

How CGI Works:
1. Concept and Previsualization: Artists and directors conceptualize the visuals, often creating storyboards or rough digital sketches (previs) to plan scenes.
2. Modeling: 3D artists use software (e.g., Autodesk Maya, Blender) to build digital models of characters, objects, or environments, defining their shape, texture, and structure.
3. Texturing and Shading: Textures (e.g., skin, metal, or landscapes) are applied to models, with shaders determining how surfaces interact with light for realism.
4. Rigging and Animation: Digital skeletons (rigs) are created for characters or objects, allowing animators to manipulate them for movement, expressions, or actions.
5. Rendering: Powerful computers process the models, textures, lighting, and animations to produce the final image or sequence. This step can be computationally intensive, often requiring render farms (networks of computers).
6. Compositing: CGI elements are integrated with live-action footage using software like Adobe After Effects or Nuke, ensuring seamless blending.
7. Post-Production: Final touches, like color grading or additional effects (e.g., explosions, weather), are added to polish the visuals.

Key Technologies and Tools:
- Software: Maya, 3ds Max, Blender, Houdini (for simulations like fire or water), and Unreal Engine (for real-time rendering).
- Hardware: High-performance GPUs, render farms, and motion capture systems to record real-world movements for digital characters.
- Techniques
- Motion Capture: Tracks actors’ movements to animate digital characters (e.g., Gollum in The Lord of the Rings).
- Particle Systems: Simulate natural phenomena like smoke, fire, or crowds.
- Ray Tracing: Creates realistic lighting and reflections for lifelike visuals.
- Real-Time Rendering: Used in modern films and games for instant visual feedback, as seen in The Mandalorian’s virtual sets (via Unreal Engine).

Applications in Film (Relevant to Montana Mischief):
For a futuristic action film like Montana Mischief, CGI would be critical for:
- Crafting dystopian Montana Mischief landscapes with sprawling cyber-cities or desolate wastelands.
- Designing futuristic vehicles, weapons, or robotic characters.
- Simulating large-scale action sequences, like explosions or aerial battles, safely and cost-effectively.
- Creating immersive IMAX-ready visuals with hyper-realistic details to captivate global audiences.


Advantages:
Enables limitless creativity (e.g., alien worlds, epic battles).
Reduces costs for complex scenes compared to practical effects.
Enhances safety by replacing dangerous stunts with digital simulations.
Challenges:
High computational and time costs for rendering complex scenes.
Requires skilled artists, increasing production budgets.
Overuse can feel artificial if not balanced with practical effects or strong storytelling.

Current Trends (2025):
AI Integration: AI tools accelerate modeling, texturing, and animation by automating repetitive tasks.
Real-Time Rendering: Tools like Unreal Engine allow filmmakers to see CGI in real-time during production, cutting costs and time.
Virtual Production: LED walls (e.g., ILM’s StageCraft) project CGI environments on set, blending live-action and digital seamlessly.

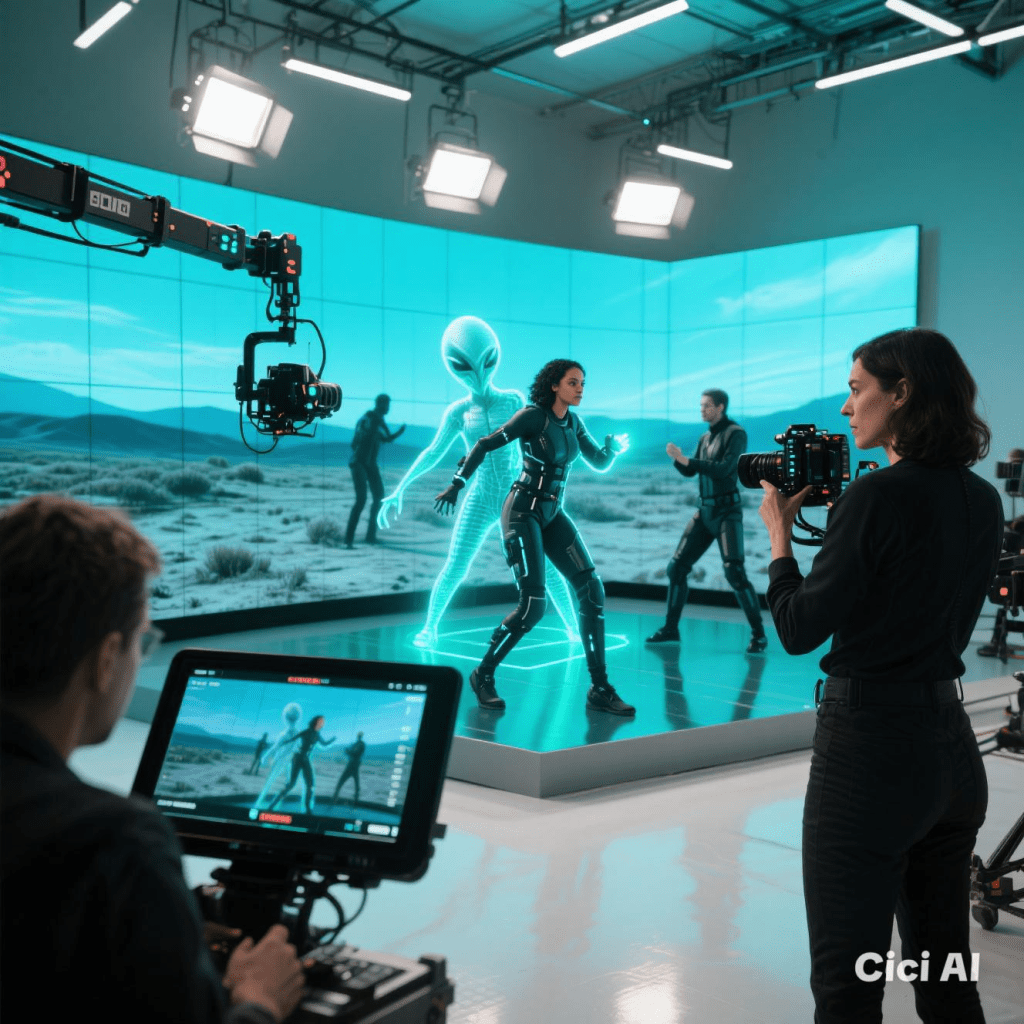


The Evolution of CGI in Film: From Pixelated Beginnings to Photorealistic Worlds

Introduction
Computer-generated imagery (CGI) has revolutionized filmmaking, transforming how stories are told and worlds are built. From its humble beginnings in the 1970s to today’s hyper-realistic digital environments, CGI has pushed the boundaries of creativity. In this blog post, we’ll explore key milestones in CGI history and how they’ve shaped modern cinema.
The Early Days: 1970s – The Birth of Digital Effects
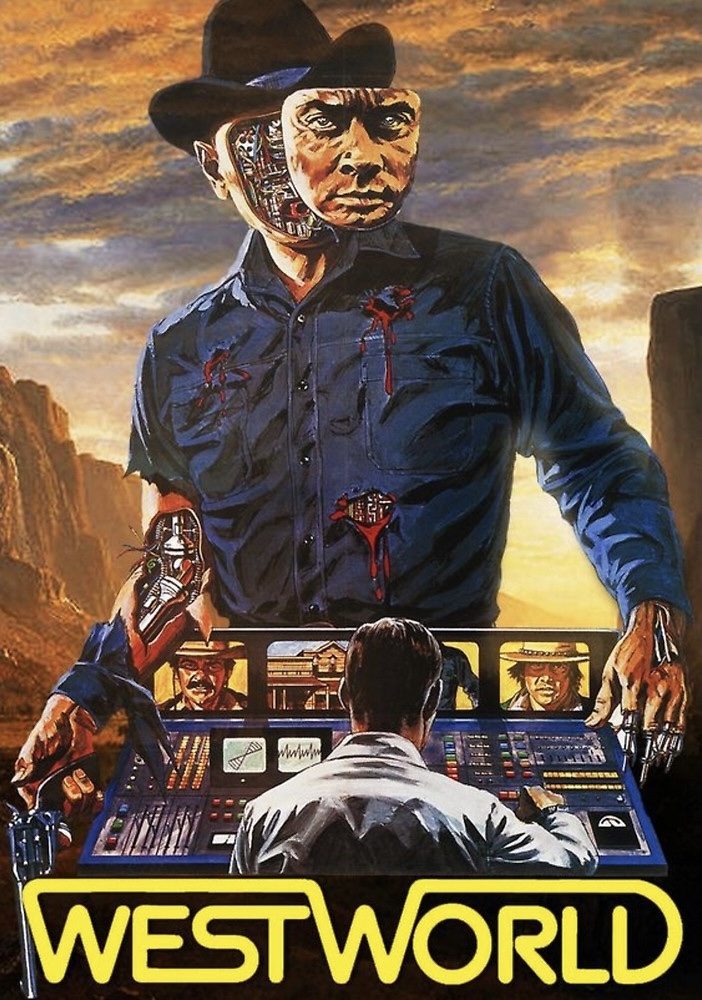
Key Film: Westworld (1973)
Breakthrough: First use of 2D CGI (pixelated POV from a robot’s vision).
Before Star Wars and Tron, Westworld introduced audiences to digital imagery with its robotic perspective—a simple but groundbreaking effect. This marked the beginning of filmmakers experimenting with computers to enhance storytelling.

The 1980s: CGI Goes Mainstream
Key Film: Tron (1982)
Breakthrough: First extensive use of 3D wireframe graphics.
Disney’s Tron was a visual marvel, immersing viewers in a neon-lit digital world. Though primitive by today’s standards, its glowing grids and light cycles set the stage for future sci-fi films.

The 1990s: The Dawn of Photorealism
Key Film: Jurassic Park (1993)
Breakthrough: First realistic CGI creatures (dinosaurs blended with animatronics).
Steven Spielberg’s Jurassic Park changed everything. For the first time, CGI creatures looked real, thanks to breakthroughs in texture mapping and motion capture. The T-Rex and raptors remain iconic to this day.

The 2000s: The Rise of Fully Digital Worlds
Key Film: Avatar (2009)
Breakthrough: Fully immersive 3D environments and performance capture.
James Cameron’s Avatar wasn’t just a movie—it was an experience. Using revolutionary motion-capture technology, CGI created the lush, alien world of Pandora, making it the highest-grossing film of its time.

The 2020s and Beyond: Hyper-Realism and AI Integration
Key Example: Montana Mischief (Futuristic Concept)
Breakthrough: AI-assisted CGI, light-code effects, and virtual production.
Modern films and shows (The Mandalorian, Dune) use real-time CGI with LED walls (StageCraft) for seamless environments. Projects like Montana Mischief (a futuristic 3030 Awakening) push boundaries with alien landscapes and digital light effects.

The Future of CGI
- AI-Generated Effects: Tools like Deep Learning can now enhance CGI faster.
- Virtual Production: LED volumes (as seen in The Volume for The Mandalorian) reduce post-production time.
- Metaverse & Film: CGI will play a huge role in interactive storytelling.

Conclusion
CGI has evolved from simple pixels to entire digital universes, forever changing cinema. As technology advances, filmmakers will continue to blend reality and imagination in ways we’ve never seen before.
What’s your favorite CGI moment in film history? Share in the comments!
#CGI #FilmHistory #VFX #MovieMagic #DigitalArt

